VARMAX models¶
This is a brief introduction notebook to VARMAX models in statsmodels. The VARMAX model is generically specified as:
where \(y_t\) is a \(\text{k_endog} \times 1\) vector.
[1]:
%matplotlib inline
[2]:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import statsmodels.api as sm
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
[3]:
dta = sm.datasets.webuse('lutkepohl2', 'https://www.stata-press.com/data/r12/')
dta.index = dta.qtr
dta.index.freq = dta.index.inferred_freq
endog = dta.loc['1960-04-01':'1978-10-01', ['dln_inv', 'dln_inc', 'dln_consump']]
Model specification¶
The VARMAX class in statsmodels allows estimation of VAR, VMA, and VARMA models (through the order argument), optionally with a constant term (via the trend argument). Exogenous regressors may also be included (as usual in statsmodels, by the exog argument), and in this way a time trend may be added. Finally, the class allows measurement error (via the measurement_error argument) and allows specifying either a diagonal or unstructured innovation covariance matrix (via the
error_cov_type argument).
Example 1: VAR¶
Below is a simple VARX(2) model in two endogenous variables and an exogenous series, but no constant term. Notice that we needed to allow for more iterations than the default (which is maxiter=50) in order for the likelihood estimation to converge. This is not unusual in VAR models which have to estimate a large number of parameters, often on a relatively small number of time series: this model, for example, estimates 27 parameters off of 75 observations of 3 variables.
[4]:
exog = endog['dln_consump']
mod = sm.tsa.VARMAX(endog[['dln_inv', 'dln_inc']], order=(2,0), trend='n', exog=exog)
res = mod.fit(maxiter=1000, disp=False)
print(res.summary())
Statespace Model Results
==================================================================================
Dep. Variable: ['dln_inv', 'dln_inc'] No. Observations: 75
Model: VARX(2) Log Likelihood 361.038
Date: Tue, 02 Feb 2021 AIC -696.076
Time: 06:54:22 BIC -665.949
Sample: 04-01-1960 HQIC -684.046
- 10-01-1978
Covariance Type: opg
===================================================================================
Ljung-Box (L1) (Q): 0.04, 10.15 Jarque-Bera (JB): 11.23, 2.37
Prob(Q): 0.84, 0.00 Prob(JB): 0.00, 0.31
Heteroskedasticity (H): 0.45, 0.40 Skew: 0.15, -0.38
Prob(H) (two-sided): 0.05, 0.03 Kurtosis: 4.87, 3.43
Results for equation dln_inv
====================================================================================
coef std err z P>|z| [0.025 0.975]
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
L1.dln_inv -0.2412 0.093 -2.593 0.010 -0.423 -0.059
L1.dln_inc 0.2947 0.449 0.657 0.511 -0.585 1.174
L2.dln_inv -0.1648 0.155 -1.061 0.288 -0.469 0.139
L2.dln_inc 0.0825 0.422 0.195 0.845 -0.745 0.910
beta.dln_consump 0.9479 0.640 1.482 0.138 -0.306 2.201
Results for equation dln_inc
====================================================================================
coef std err z P>|z| [0.025 0.975]
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
L1.dln_inv 0.0633 0.036 1.768 0.077 -0.007 0.133
L1.dln_inc 0.0841 0.107 0.783 0.434 -0.126 0.295
L2.dln_inv 0.0097 0.033 0.296 0.768 -0.055 0.074
L2.dln_inc 0.0339 0.134 0.253 0.801 -0.229 0.297
beta.dln_consump 0.7711 0.112 6.872 0.000 0.551 0.991
Error covariance matrix
============================================================================================
coef std err z P>|z| [0.025 0.975]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sqrt.var.dln_inv 0.0434 0.004 12.289 0.000 0.036 0.050
sqrt.cov.dln_inv.dln_inc 4.755e-05 0.002 0.024 0.981 -0.004 0.004
sqrt.var.dln_inc 0.0109 0.001 11.220 0.000 0.009 0.013
============================================================================================
Warnings:
[1] Covariance matrix calculated using the outer product of gradients (complex-step).
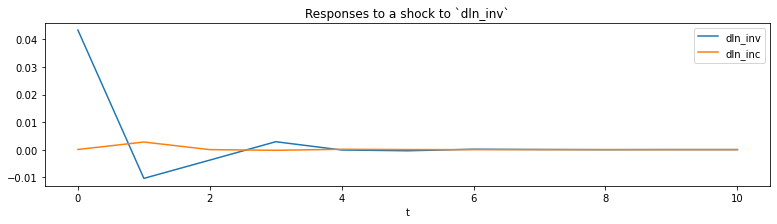
From the estimated VAR model, we can plot the impulse response functions of the endogenous variables.
[5]:
ax = res.impulse_responses(10, orthogonalized=True).plot(figsize=(13,3))
ax.set(xlabel='t', title='Responses to a shock to `dln_inv`');
[5]:
[Text(0.5, 0, 't'), Text(0.5, 1.0, 'Responses to a shock to `dln_inv`')]
Example 2: VMA¶
A vector moving average model can also be formulated. Below we show a VMA(2) on the same data, but where the innovations to the process are uncorrelated. In this example we leave out the exogenous regressor but now include the constant term.
[6]:
mod = sm.tsa.VARMAX(endog[['dln_inv', 'dln_inc']], order=(0,2), error_cov_type='diagonal')
res = mod.fit(maxiter=1000, disp=False)
print(res.summary())
Statespace Model Results
==================================================================================
Dep. Variable: ['dln_inv', 'dln_inc'] No. Observations: 75
Model: VMA(2) Log Likelihood 353.886
+ intercept AIC -683.771
Date: Tue, 02 Feb 2021 BIC -655.961
Time: 06:54:27 HQIC -672.667
Sample: 04-01-1960
- 10-01-1978
Covariance Type: opg
===================================================================================
Ljung-Box (L1) (Q): 0.01, 0.07 Jarque-Bera (JB): 12.35, 12.99
Prob(Q): 0.93, 0.78 Prob(JB): 0.00, 0.00
Heteroskedasticity (H): 0.44, 0.81 Skew: 0.05, -0.48
Prob(H) (two-sided): 0.04, 0.60 Kurtosis: 4.99, 4.80
Results for equation dln_inv
=================================================================================
coef std err z P>|z| [0.025 0.975]
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
intercept 0.0182 0.005 3.824 0.000 0.009 0.028
L1.e(dln_inv) -0.2620 0.106 -2.481 0.013 -0.469 -0.055
L1.e(dln_inc) 0.5405 0.633 0.854 0.393 -0.700 1.781
L2.e(dln_inv) 0.0298 0.148 0.201 0.841 -0.261 0.320
L2.e(dln_inc) 0.1630 0.477 0.341 0.733 -0.773 1.099
Results for equation dln_inc
=================================================================================
coef std err z P>|z| [0.025 0.975]
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
intercept 0.0207 0.002 13.123 0.000 0.018 0.024
L1.e(dln_inv) 0.0489 0.041 1.178 0.239 -0.032 0.130
L1.e(dln_inc) -0.0806 0.139 -0.580 0.562 -0.353 0.192
L2.e(dln_inv) 0.0174 0.042 0.410 0.682 -0.066 0.101
L2.e(dln_inc) 0.1278 0.152 0.842 0.400 -0.170 0.425
Error covariance matrix
==================================================================================
coef std err z P>|z| [0.025 0.975]
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sigma2.dln_inv 0.0020 0.000 7.344 0.000 0.001 0.003
sigma2.dln_inc 0.0001 2.32e-05 5.834 0.000 9.01e-05 0.000
==================================================================================
Warnings:
[1] Covariance matrix calculated using the outer product of gradients (complex-step).
/home/travis/build/statsmodels/statsmodels/statsmodels/base/model.py:568: ConvergenceWarning: Maximum Likelihood optimization failed to converge. Check mle_retvals
ConvergenceWarning)
Caution: VARMA(p,q) specifications¶
Although the model allows estimating VARMA(p,q) specifications, these models are not identified without additional restrictions on the representation matrices, which are not built-in. For this reason, it is recommended that the user proceed with error (and indeed a warning is issued when these models are specified). Nonetheless, they may in some circumstances provide useful information.
[7]:
mod = sm.tsa.VARMAX(endog[['dln_inv', 'dln_inc']], order=(1,1))
res = mod.fit(maxiter=1000, disp=False)
print(res.summary())
/home/travis/build/statsmodels/statsmodels/statsmodels/tsa/statespace/varmax.py:163: EstimationWarning: Estimation of VARMA(p,q) models is not generically robust, due especially to identification issues.
EstimationWarning)
Statespace Model Results
==================================================================================
Dep. Variable: ['dln_inv', 'dln_inc'] No. Observations: 75
Model: VARMA(1,1) Log Likelihood 354.287
+ intercept AIC -682.575
Date: Tue, 02 Feb 2021 BIC -652.448
Time: 06:54:29 HQIC -670.545
Sample: 04-01-1960
- 10-01-1978
Covariance Type: opg
===================================================================================
Ljung-Box (L1) (Q): 0.01, 0.06 Jarque-Bera (JB): 11.05, 14.18
Prob(Q): 0.94, 0.81 Prob(JB): 0.00, 0.00
Heteroskedasticity (H): 0.43, 0.91 Skew: 0.01, -0.46
Prob(H) (two-sided): 0.04, 0.81 Kurtosis: 4.88, 4.92
Results for equation dln_inv
=================================================================================
coef std err z P>|z| [0.025 0.975]
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
intercept 0.0105 0.066 0.160 0.873 -0.118 0.139
L1.dln_inv -0.0061 0.697 -0.009 0.993 -1.372 1.359
L1.dln_inc 0.3804 2.768 0.137 0.891 -5.044 5.805
L1.e(dln_inv) -0.2487 0.707 -0.352 0.725 -1.635 1.138
L1.e(dln_inc) 0.1253 3.017 0.042 0.967 -5.788 6.038
Results for equation dln_inc
=================================================================================
coef std err z P>|z| [0.025 0.975]
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
intercept 0.0165 0.027 0.601 0.548 -0.037 0.070
L1.dln_inv -0.0336 0.278 -0.121 0.904 -0.579 0.512
L1.dln_inc 0.2349 1.117 0.210 0.833 -1.955 2.425
L1.e(dln_inv) 0.0888 0.285 0.312 0.755 -0.470 0.647
L1.e(dln_inc) -0.2376 1.152 -0.206 0.837 -2.495 2.020
Error covariance matrix
============================================================================================
coef std err z P>|z| [0.025 0.975]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sqrt.var.dln_inv 0.0449 0.003 14.533 0.000 0.039 0.051
sqrt.cov.dln_inv.dln_inc 0.0017 0.003 0.649 0.516 -0.003 0.007
sqrt.var.dln_inc 0.0116 0.001 11.717 0.000 0.010 0.013
============================================================================================
Warnings:
[1] Covariance matrix calculated using the outer product of gradients (complex-step).