VARMAX models¶
This is a brief introduction notebook to VARMAX models in statsmodels. The VARMAX model is generically specified as:
where
[1]:
%matplotlib inline
[2]:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import statsmodels.api as sm
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
[3]:
dta = sm.datasets.webuse('lutkepohl2', 'https://www.stata-press.com/data/r12/')
dta.index = dta.qtr
dta.index.freq = dta.index.inferred_freq
endog = dta.loc['1960-04-01':'1978-10-01', ['dln_inv', 'dln_inc', 'dln_consump']]
Model specification¶
The VARMAX class in statsmodels allows estimation of VAR, VMA, and VARMA models (through the order argument), optionally with a constant term (via the trend argument). Exogenous regressors may also be included (as usual in statsmodels, by the exog argument), and in this way a time trend may be added. Finally, the class allows measurement error (via the measurement_error argument) and allows specifying either a diagonal or unstructured innovation covariance matrix (via the
error_cov_type argument).
Example 1: VAR¶
Below is a simple VARX(2) model in two endogenous variables and an exogenous series, but no constant term. Notice that we needed to allow for more iterations than the default (which is maxiter=50) in order for the likelihood estimation to converge. This is not unusual in VAR models which have to estimate a large number of parameters, often on a relatively small number of time series: this model, for example, estimates 27 parameters off of 75 observations of 3 variables.
[4]:
exog = endog['dln_consump']
mod = sm.tsa.VARMAX(endog[['dln_inv', 'dln_inc']], order=(2,0), trend='n', exog=exog)
res = mod.fit(maxiter=1000, disp=False)
print(res.summary())
Statespace Model Results
==================================================================================
Dep. Variable: ['dln_inv', 'dln_inc'] No. Observations: 75
Model: VARX(2) Log Likelihood 361.037
Date: Wed, 02 Nov 2022 AIC -696.075
Time: 17:07:51 BIC -665.947
Sample: 04-01-1960 HQIC -684.045
- 10-01-1978
Covariance Type: opg
===================================================================================
Ljung-Box (L1) (Q): 0.05, 10.07 Jarque-Bera (JB): 11.05, 2.46
Prob(Q): 0.82, 0.00 Prob(JB): 0.00, 0.29
Heteroskedasticity (H): 0.45, 0.40 Skew: 0.16, -0.38
Prob(H) (two-sided): 0.05, 0.03 Kurtosis: 4.85, 3.44
Results for equation dln_inv
====================================================================================
coef std err z P>|z| [0.025 0.975]
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
L1.dln_inv -0.2399 0.093 -2.578 0.010 -0.422 -0.058
L1.dln_inc 0.2776 0.449 0.618 0.536 -0.602 1.157
L2.dln_inv -0.1654 0.155 -1.066 0.286 -0.470 0.139
L2.dln_inc 0.0643 0.421 0.153 0.879 -0.761 0.889
beta.dln_consump 0.9840 0.637 1.545 0.122 -0.264 2.232
Results for equation dln_inc
====================================================================================
coef std err z P>|z| [0.025 0.975]
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
L1.dln_inv 0.0633 0.036 1.770 0.077 -0.007 0.133
L1.dln_inc 0.0803 0.107 0.750 0.453 -0.129 0.290
L2.dln_inv 0.0111 0.033 0.337 0.736 -0.054 0.076
L2.dln_inc 0.0335 0.134 0.250 0.803 -0.229 0.296
beta.dln_consump 0.7756 0.113 6.893 0.000 0.555 0.996
Error covariance matrix
============================================================================================
coef std err z P>|z| [0.025 0.975]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sqrt.var.dln_inv 0.0434 0.004 12.295 0.000 0.036 0.050
sqrt.cov.dln_inv.dln_inc 6.006e-05 0.002 0.030 0.976 -0.004 0.004
sqrt.var.dln_inc 0.0109 0.001 11.212 0.000 0.009 0.013
============================================================================================
Warnings:
[1] Covariance matrix calculated using the outer product of gradients (complex-step).
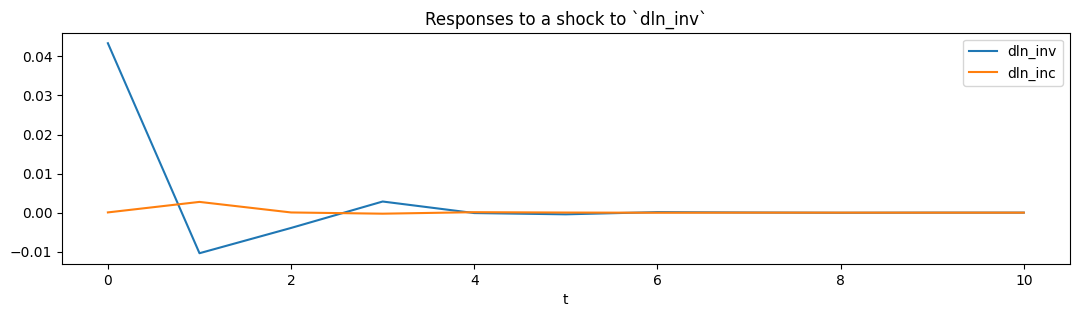
From the estimated VAR model, we can plot the impulse response functions of the endogenous variables.
[5]:
ax = res.impulse_responses(10, orthogonalized=True, impulse=[1, 0]).plot(figsize=(13,3))
ax.set(xlabel='t', title='Responses to a shock to `dln_inv`');
Example 2: VMA¶
A vector moving average model can also be formulated. Below we show a VMA(2) on the same data, but where the innovations to the process are uncorrelated. In this example we leave out the exogenous regressor but now include the constant term.
[6]:
mod = sm.tsa.VARMAX(endog[['dln_inv', 'dln_inc']], order=(0,2), error_cov_type='diagonal')
res = mod.fit(maxiter=1000, disp=False)
print(res.summary())
Statespace Model Results
==================================================================================
Dep. Variable: ['dln_inv', 'dln_inc'] No. Observations: 75
Model: VMA(2) Log Likelihood 353.883
+ intercept AIC -683.766
Date: Wed, 02 Nov 2022 BIC -655.956
Time: 17:07:56 HQIC -672.661
Sample: 04-01-1960
- 10-01-1978
Covariance Type: opg
===================================================================================
Ljung-Box (L1) (Q): 0.02, 0.05 Jarque-Bera (JB): 11.85, 13.52
Prob(Q): 0.88, 0.83 Prob(JB): 0.00, 0.00
Heteroskedasticity (H): 0.44, 0.81 Skew: 0.05, -0.48
Prob(H) (two-sided): 0.05, 0.60 Kurtosis: 4.95, 4.84
Results for equation dln_inv
=================================================================================
coef std err z P>|z| [0.025 0.975]
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
intercept 0.0182 0.005 3.815 0.000 0.009 0.028
L1.e(dln_inv) -0.2710 0.105 -2.579 0.010 -0.477 -0.065
L1.e(dln_inc) 0.5424 0.631 0.859 0.390 -0.695 1.780
L2.e(dln_inv) 0.0397 0.146 0.271 0.786 -0.247 0.326
L2.e(dln_inc) 0.1665 0.478 0.348 0.728 -0.770 1.103
Results for equation dln_inc
=================================================================================
coef std err z P>|z| [0.025 0.975]
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
intercept 0.0207 0.002 12.977 0.000 0.018 0.024
L1.e(dln_inv) 0.0483 0.042 1.158 0.247 -0.033 0.130
L1.e(dln_inc) -0.0742 0.140 -0.532 0.595 -0.348 0.199
L2.e(dln_inv) 0.0172 0.042 0.406 0.685 -0.066 0.100
L2.e(dln_inc) 0.1313 0.152 0.861 0.389 -0.168 0.430
Error covariance matrix
==================================================================================
coef std err z P>|z| [0.025 0.975]
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sigma2.dln_inv 0.0020 0.000 7.384 0.000 0.001 0.003
sigma2.dln_inc 0.0001 2.34e-05 5.812 0.000 9e-05 0.000
==================================================================================
Warnings:
[1] Covariance matrix calculated using the outer product of gradients (complex-step).
Caution: VARMA(p,q) specifications¶
Although the model allows estimating VARMA(p,q) specifications, these models are not identified without additional restrictions on the representation matrices, which are not built-in. For this reason, it is recommended that the user proceed with error (and indeed a warning is issued when these models are specified). Nonetheless, they may in some circumstances provide useful information.
[7]:
mod = sm.tsa.VARMAX(endog[['dln_inv', 'dln_inc']], order=(1,1))
res = mod.fit(maxiter=1000, disp=False)
print(res.summary())
/opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.10.8/x64/lib/python3.10/site-packages/statsmodels/tsa/statespace/varmax.py:161: EstimationWarning: Estimation of VARMA(p,q) models is not generically robust, due especially to identification issues.
warn('Estimation of VARMA(p,q) models is not generically robust,'
Statespace Model Results
==================================================================================
Dep. Variable: ['dln_inv', 'dln_inc'] No. Observations: 75
Model: VARMA(1,1) Log Likelihood 354.290
+ intercept AIC -682.580
Date: Wed, 02 Nov 2022 BIC -652.452
Time: 17:07:58 HQIC -670.550
Sample: 04-01-1960
- 10-01-1978
Covariance Type: opg
===================================================================================
Ljung-Box (L1) (Q): 0.00, 0.05 Jarque-Bera (JB): 11.18, 13.96
Prob(Q): 0.96, 0.82 Prob(JB): 0.00, 0.00
Heteroskedasticity (H): 0.43, 0.91 Skew: 0.01, -0.45
Prob(H) (two-sided): 0.04, 0.81 Kurtosis: 4.89, 4.91
Results for equation dln_inv
=================================================================================
coef std err z P>|z| [0.025 0.975]
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
intercept 0.0104 0.066 0.159 0.874 -0.118 0.139
L1.dln_inv -0.0051 0.704 -0.007 0.994 -1.385 1.375
L1.dln_inc 0.3827 2.766 0.138 0.890 -5.039 5.805
L1.e(dln_inv) -0.2475 0.714 -0.347 0.729 -1.647 1.152
L1.e(dln_inc) 0.1232 3.017 0.041 0.967 -5.791 6.037
Results for equation dln_inc
=================================================================================
coef std err z P>|z| [0.025 0.975]
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
intercept 0.0165 0.027 0.600 0.548 -0.037 0.070
L1.dln_inv -0.0328 0.282 -0.117 0.907 -0.585 0.519
L1.dln_inc 0.2351 1.114 0.211 0.833 -1.947 2.418
L1.e(dln_inv) 0.0887 0.288 0.308 0.758 -0.476 0.654
L1.e(dln_inc) -0.2393 1.148 -0.208 0.835 -2.490 2.012
Error covariance matrix
============================================================================================
coef std err z P>|z| [0.025 0.975]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sqrt.var.dln_inv 0.0449 0.003 14.527 0.000 0.039 0.051
sqrt.cov.dln_inv.dln_inc 0.0017 0.003 0.652 0.514 -0.003 0.007
sqrt.var.dln_inc 0.0116 0.001 11.729 0.000 0.010 0.013
============================================================================================
Warnings:
[1] Covariance matrix calculated using the outer product of gradients (complex-step).